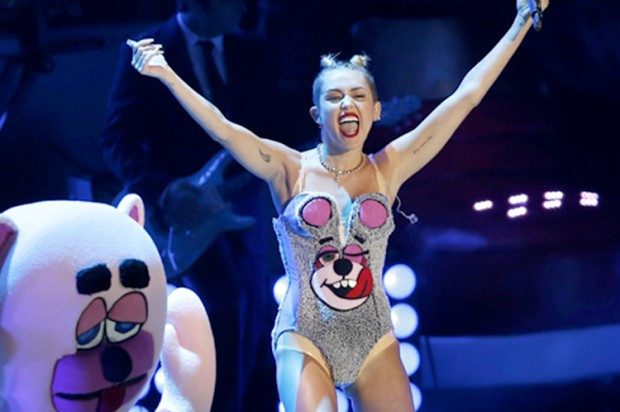
Here is what I can tell you. When I was in New York a month ago and one night someone suggested we go to an MTV party, the first thought I had was — wait, MTV still exists?
But I guess it does because this week I’ve spent a lot of time talking about MTV. Well, not really so much MTV as the MTV Video Music Awards. Well, not even that, so much as Miley Cyrus’s performance. Yeah, I’ve spent a lot of time talking about Miley Cyrus’s performance at the VMAs. And so has the rest of America. Not only was a story about her performance the main event on the CNN homepage the next day, I then saw The Onion’s fictional op-ed, ostensibly written by the managing editor of CNN.com, with the headline, “Let Me Explain Why Miley Cyrus’ VMA Performance Was Our Top Story This Morning” (CNN spoiler alert: ad revenue), retweeted in my feed no less than 9 times in a matter of hours (The Onion spoiler alert: ad revenue).
For a culture that has become desensitized to multi-million dollar celebrity media empires built off the backs of sex tapes, something about Cyrus’s performance nevertheless managed to strike a nerve.
Here’s what we saw:
Afterwards, I don’t think any of us were quite sure exactly what had just happened to us.
It wasn’t just the raunchiness or the shock value. This is the VMA’s, after all, where Madonna kicked things off 30 years ago by dry humping the stage in a punk wedding dress; where Britney sang “I’m a Slave 4 u” while dancing in a green version of Cyrus’s flesh-toned 2-piece, with a live python draped around her body, and later where Madonna and Britney and Christina all made out, and then after that, where Lady Gaga hanged herself. The controversial VMA performance is now pretty much a traditional rite of passage in the transition from Disney child star into adult entertainer.
Wait… what?
Anyway, we expect this. We’re practically inured to it at this point. But this show, Cyrus’s show, got under our skin. And not in, like, a good way.
“It seems everyone hated whatever it was Miley Cyrus was doing at last night’s VMAs,” Neetzan Zimmerman wrote on Gawker.
Whatever it was she was doing…. we couldn’t even be sure. The next morning we woke up in turns “stunned,” “shocked,” “outraged,” outraged by the outrage. From the moment Cyrus first stuck out her tongue, things felt weird. We’re so used to performers adhering to a strict code of conduct of media training — gliding through precise sequences of polished, camera-ready choreography. You want this to wind up being the image that follows you around the internet tomorrow, we thought to ourselves watching Cyrus gag.
Little did we know.
Then the performance began in earnest, Cyrus singing and dancing to her summer jam, “We Can’t Stop,” and we tried to relax. But 90 seconds in, as Jody Rosen writes on the Vulture blog, “pausing to spank and simulate analingus upon the ass of a thickly set African-American backup dancer, her act tipped over into what we may as well just call racism: a minstrel show routine whose ghoulishness was heightened by Cyrus’s madcap charisma.”
Awkward.
And that was all before Robin Thicke got onstage and Cyrus snapped out of her teddy-bear teddy, down to a nude, vinyl bikini, to duet Thicke’s own controversial summer hit, “Blurred Lines,” and the REALLY uncomfortable shit happened. The most disconcerting thing about their performance was Thicke’s consistent lack of….. engagement. While Cyrus twerked all over his body, Thicke seemed barely aware she was there. The New York Times described Cyrus’s behavior as a “molesting” of Robin Thicke. Behind his shades you couldn’t be sure whether he was even making eye contact. Of course, what Thicke was doing was reenacting the Blurred Lines video. Directed by Diane Martel, who’s also responsible for the video for We Can’t Stop, the video features basically completely naked women dancing next to, strutting past, facing away from, and engaging in a host of other activities that in general involve pretty much anything except actually acknowledging the presence of Robin Thicke. Or of T.I. or Pharrell Williams. The non-interactions between the fully-dressed men in the video and naked women seem so unaligned and asynchronous and non-sequitured they might as well be SnapChatting them in. “I directed the girls to look into the camera,” Martel explained on Grantland. “This is very intentional and they do it most of the time; they are in the power position. I wanted to deal with the misogynist, funny lyrics in a way where the girls were going to overpower the men. Look at Emily Ratajkowski’s performance; it’s very, very funny and subtly ridiculing. I find [the video] meta and playful.”
Whether the end result really succeeds in its intention is debatable (“Is meta-nudity a thing? Is there such thing as ‘ironic objectification?'” Callie Beusman asks on Jezebel), but this conceit at least makes sense in the context of a music video — and, by the way, subconsciously speaks to all of us and our modern experience of hyper-mediated, asynchronous connection. But you know where it doesn’t actually work? Live, on stage, as a visual to support a 20-year old former child star’s transformation into a woman claiming her sexuality.
“Performing near-nude on the VMA stage 10 years earlier,” Daniel D’addario writes on Salon.com, “Christina Aguilera was singing an ode to her own empowerment and desire to get sexual satisfaction on her own terms. Last night, Miley was singing a song about how good Robin Thicke is at sex.” And in this context, Thicke’s lack of engagement in the proceedings made Cyrus’s relentless hypersexualization look desperate, or worse yet, depraved. At first Cyrus came across like that girl you knew in college, drunk at a party, looking to fuck for validation. If you happened to stop to factor in the 16 year age difference between Thicke and Cyrus, a whole other kind of psychological issue could, conceivably, have seemed to be spilling itself out all over MTV. But the real cringe-worthy element of the experience was that, in the absence of active participation — and its implicit consent — from anyone sharing the stage with her, Cyrus’s agrosexual zeal very quickly began to look kinda….uhm…. predatory.
In one singular moment, Cyrus appeared to us as victim and predator. The violated, and the violator. No wonder we weren’t sure what we were even looking at. Cognitive dissonance, haaaaaaaay! Miley Cyrus had roofied us all. You could understand why, the next morning, MSNBC’s, Mika Brzezinski would call her “disturbed.”
Perhaps the problem is that “no one has apparently said ‘no’ [to Cyrus] for the last six months,” Jon Carmanica, suggested in The New York Times.
But it sure did make for some great GIFs tho, amirite?!

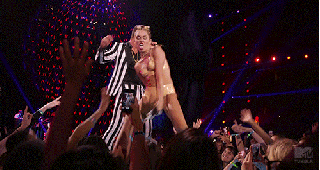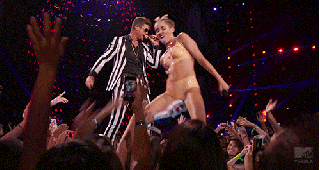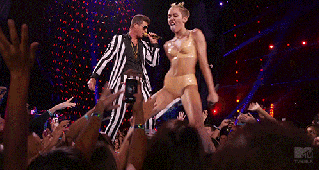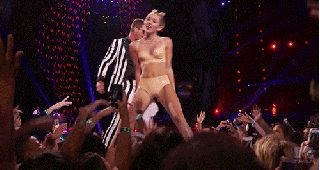

From its very first steps, Cyrus’s performance felt, unmistakably, like watching a GIF happen in real-time. On the Atlantic, Nolan Feeney called this “the most GIFable award show ever,” and, indeed, Cyrus’s performance felt like the first one truly made for the age of the Internet. The act was speaking the native tongue — stuck all the way out — of the digital age, its direct appeal to meme culture as blatant and aggressive as the display of sexuality. All the performances before it had been made for TV. This show changed that. The source material and its inevitable meme-ification appeared to be happening simultaneously. The Internet was inherently integrated within the performance. It was no longer a “second” screen; it was the same damn screen. If you go to watch the performance now on MTV.com, a bright pink button, set in stark relief against the site’s black background, blares, “GIF THIS!”
You want this to wind up being the image that follows you around the internet tomorrow?
Yes. That was the whole point.
It’s our party we can do what we want
It’s our party we can say what we want
It’s our party we can love who we want
We can kiss who we want
We can sing what we want
– “We Can’t Stop“
Six years before Cyrus was even born, a trio of dudes demanded you had to fight for your right to party. But that’s not what We Can’t Stop is is about. This song is a rallying cry for the right to be your own person. Something the human collateral of the Disney industrial complex, and the daughter of a Hollywood dad, would know something about, no doubt. (“It’s my mouth; I can say what I want to.”) But it’s also something that any adolescent can relate to, especially now.
“It’s like a giant, fucked-up selfie,” Martel said, explaining the concept behind the “We Can’t Stop” video, on RollingStone.com. “She’s absolutely taking the piss out of being in a pop video.” Even if you haven’t had to shoulder the weight of a multi-million dollar entertainment franchise since you were a child, everyone growing up now is saddled with the responsibility of managing their mediated identities. So how do you rebel against that responsibility? How do you subvert the expectation to maintain your put-together, meticulously edited persona? Maybe you have a video of yourself doing a Salvia bong hit at a house party on your 18th birthday end up on TMZ. Maybe you fuck your image up. You don’t try to look good. You grimace and stick your tongue out and take a photo and post that fucked-up selfie for the world to see.
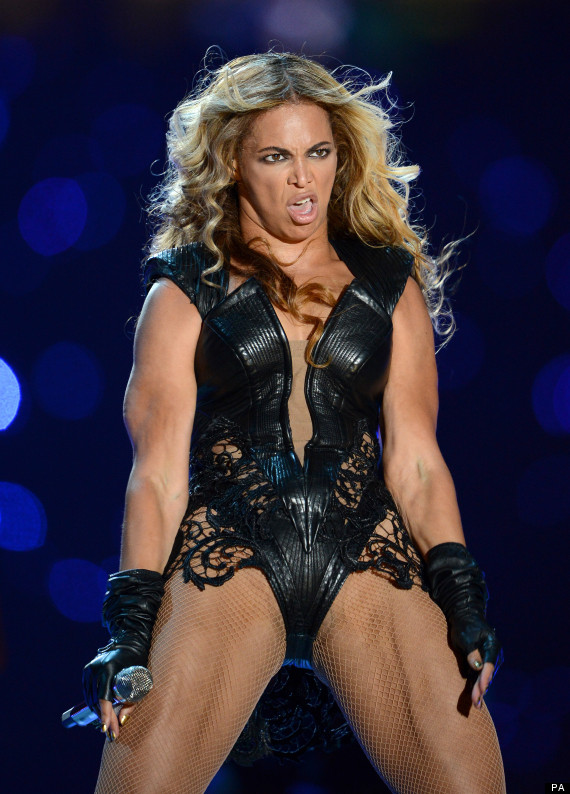
Because if you don’t do it on your terms, the Internet meme hive force will do it for you. Here’s a pic that made the Internet meme rounds in the wake of Beyonce’s Super Bowl performance earlier this year:

And here’s Cyrus fucking the shot up on purpose, before you could do it to her:
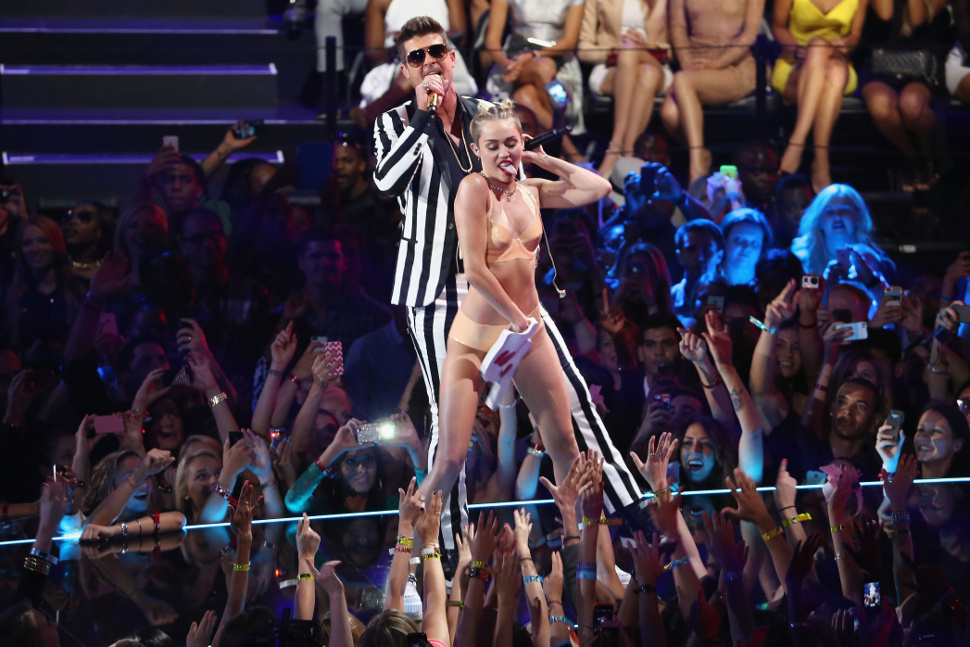

If you think Cyrus was trying to look good for you, if you think that no one was telling her “no” as she was putting the VMA performance together, that she herself wasn’t scrutinizing each frame of rehearsal video, and keenly understanding just how wrong it all looked, you’re completely missing the point.
We live in an age of violation. From News of the World hacking the cell phones of celebrities and bombing victims, to PRISM hacking everyone, everything, all the time. From doxxing to TMZ, from Wikileaks to Kiki Kannibal to Star Wars Kid to so many victims of online harassment driven to suicide, to Diana dying in a car crash in a French tunnel while being chased by paparazzi, to “Sad Keanu.”
The meme hive force is the digestive system of our networked world, capable of gleefully devouring its victims — or at least its objects — alive. Cyrus doing it to herself is “disturbed,” but the violating, exploiting meme hive force doing it to her is just another Tuesday on the Internet? And we’re totally cool with that. But, see, Cyrus thinks this is her song. And she can sing if she wants to. Her performance, crass, lewd, uncomfortable, disturbing, whatever, turned the hive force dynamic on its head. The meme object rolled out of a giant teddy bear, landed on stage and screamed, “GIF THIS!” It stuck its tongue out at all of us and belted, FIRST! at the top of its lungs and memed itself. Before anyone else could. The show got the upper hand by turning itself into the object of its own violation.
Because when we’ve already been titillated in every way imaginable, what else is there left to do? Cyrus basically didn’t do anything on the VMA stage that hasn’t been simulated there in one way or another before. So how else is there for a female pop star to traffic in her own sexuality in any new way, except to make us all feel like she was coercing us into violating her?
It was a new one for me. Was it weird for you, too?
“The Internet is fickle,” Martel said on Grantland, “But if a video is strong and entertaining, it is going to get massive hits, so of course strong work is going to have an effect on record sales. As I said, I’m mega-focused on selling records right now, so I’m doing that. I’m only taking jobs where this is a possibility. There is a new generation of kids that are overstimulated as viewers and you have to address that somehow. I’m just paying attention to the audience and their movements.”
What I learned from the 2013 VMAs is that owning your sexuality is passé, but owning meme culture by exploiting your sexuality is now. After all, in the attention economy, self-exploitation is self-empowerment. (Miley Cyrus spoiler alert: ad revenue).
Whatever you think of it, Cyrus’s performance was a deliberate reflection of where we are as culture. Calling it a “commentary” may be an overstatement, but it’s definitely a comment:
R U NOT ENTERTAINED?????

Oh, and guess what else? MTV, it turns out, still exists.
 Image: Culture Wins
Image: Culture Wins